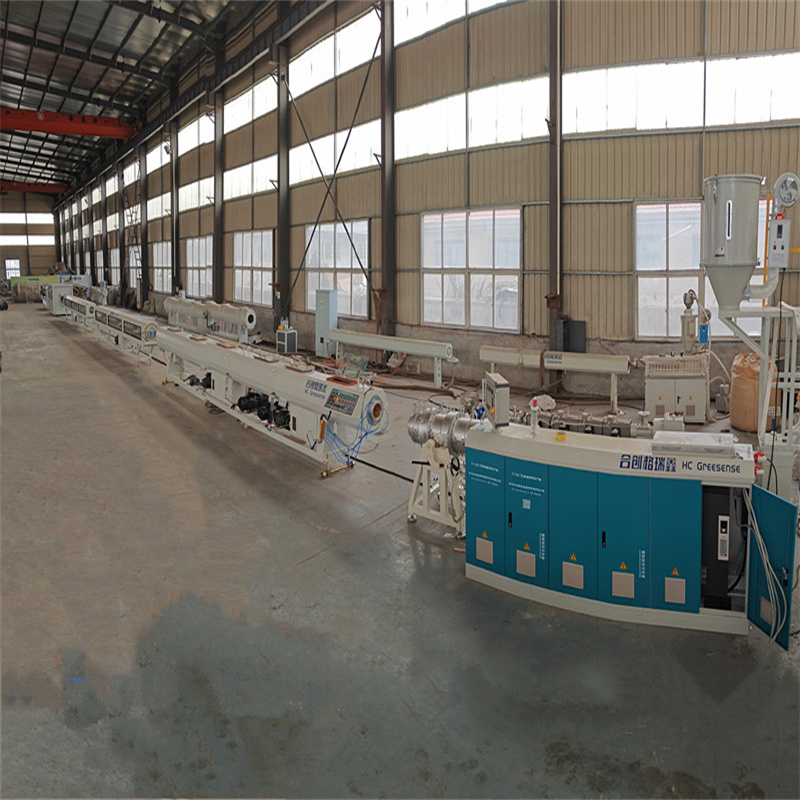
Corrugated Pipe Extrusion Line
Send Inquiry
Corrugated Pipe Extrusion Line Production Process
1. Material Feeding:
Raw polymer pellets are fed into the extruder hopper.
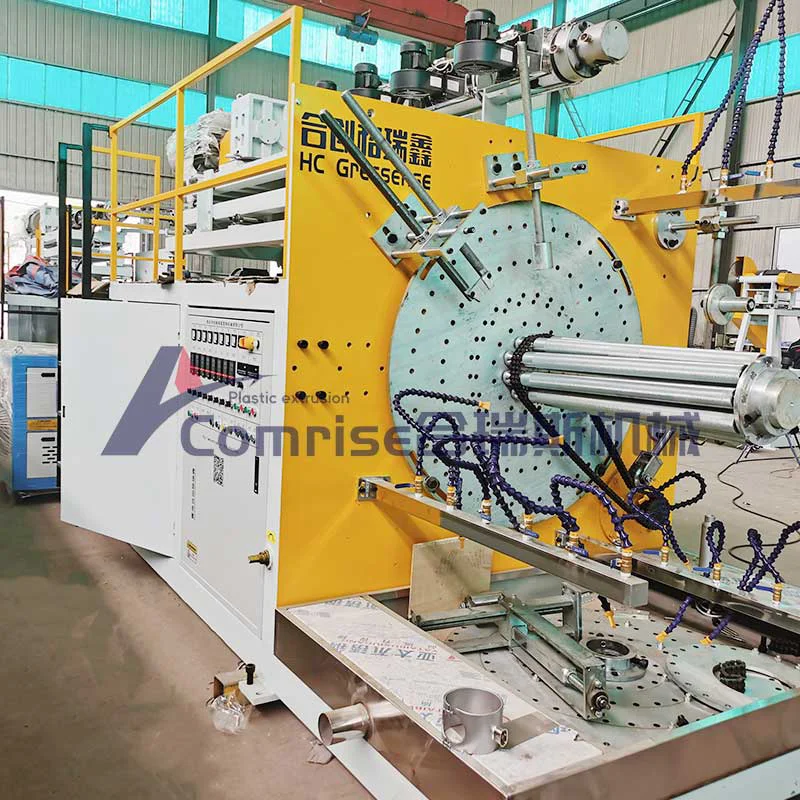
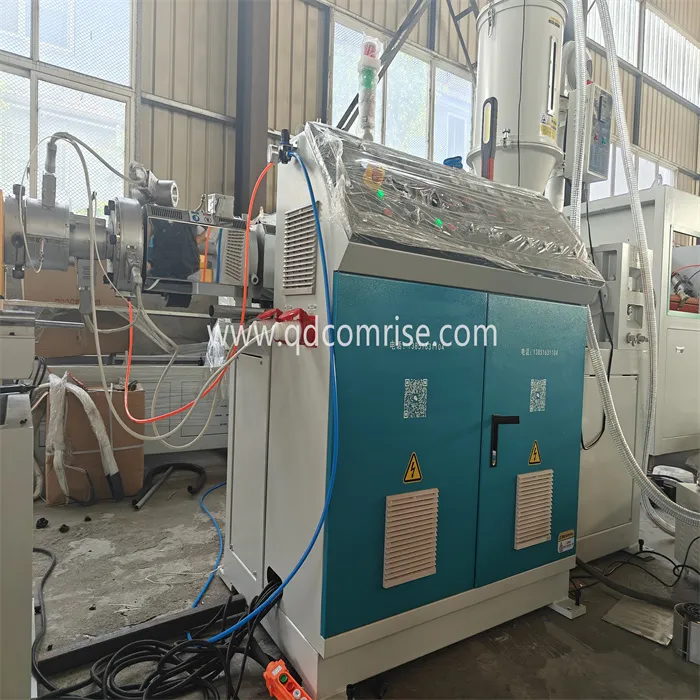
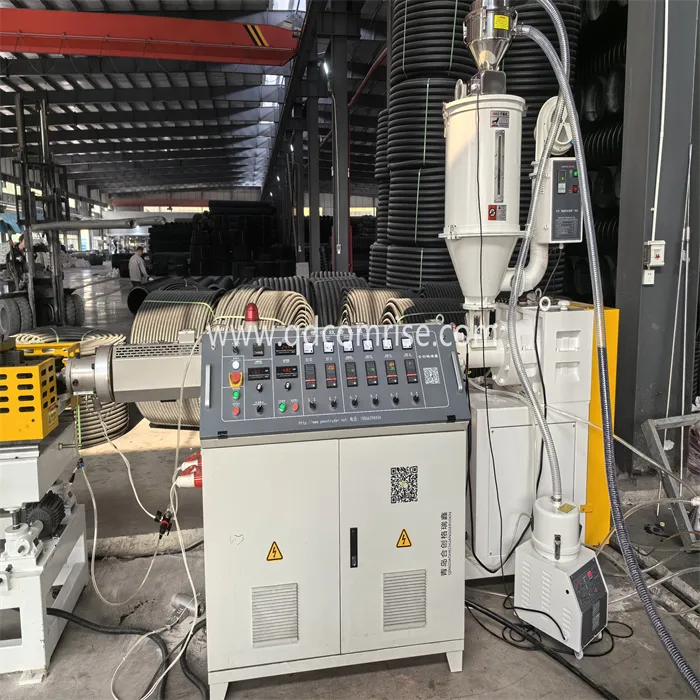
2. Extrusion:
The extruder melts the polymer and forces it through the die head to form a smooth pipe.
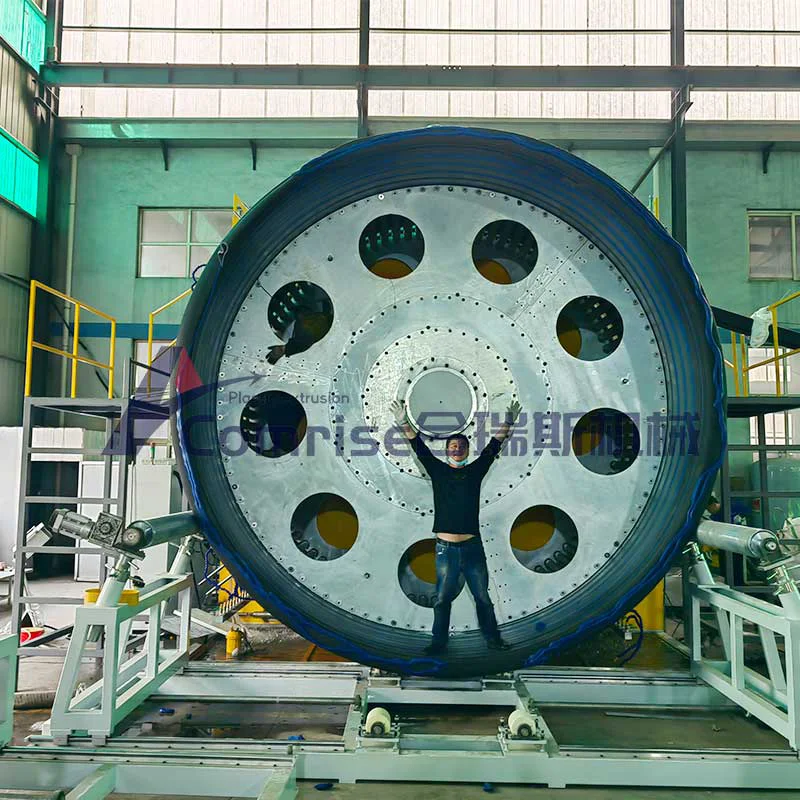
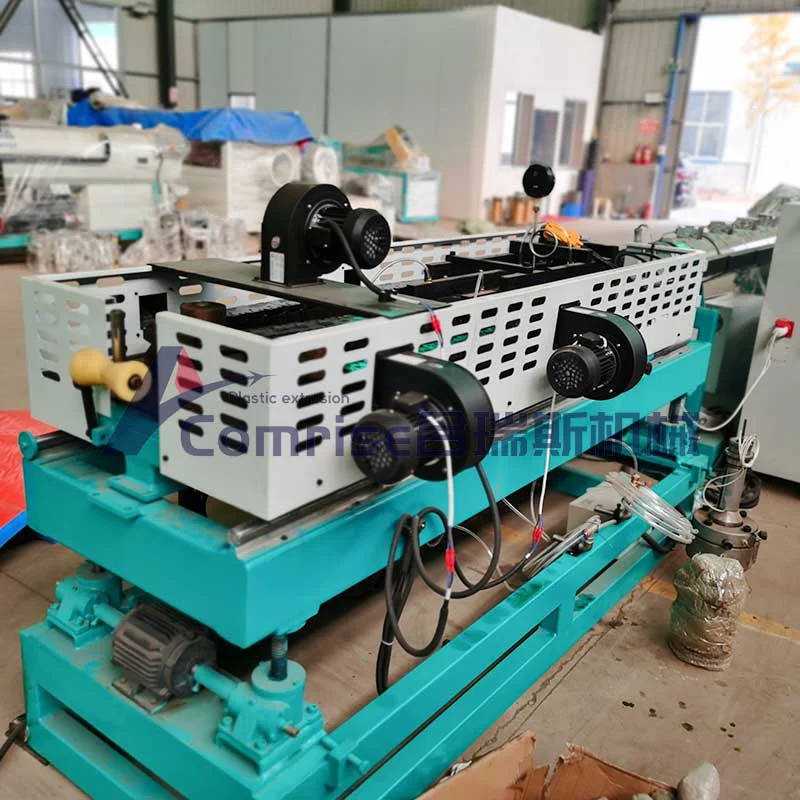
3. Corrugation:
The pipe enters the corrugator, where it is shaped into a corrugated profile using mold blocks and vacuum pressure.
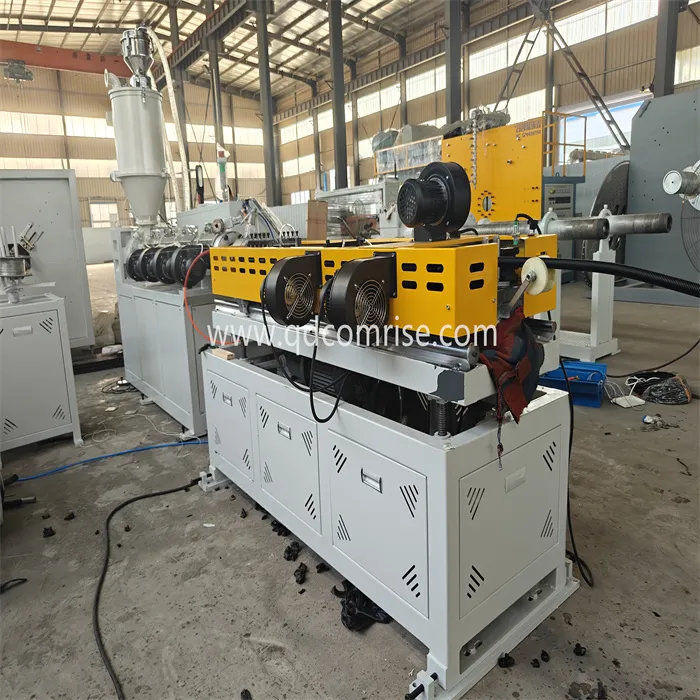
4. Cooling:
The corrugated pipe is cooled to solidify its structure.
5. HaulOff and Cutting:
The pipe is pulled through the line by the hauloff unit and cut to the required length.
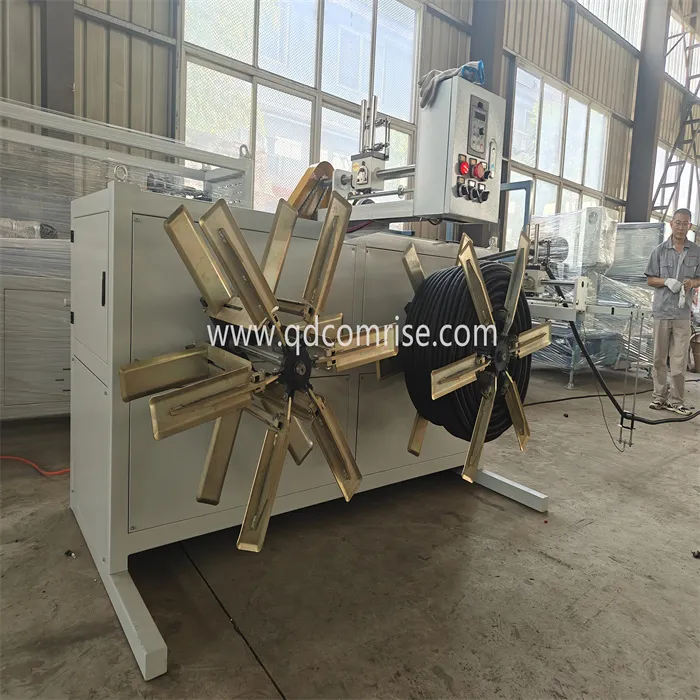
6. Stacking or Coiling:
The finished pipes are stacked or coiled for storage and transportation.
Corrugated Pipe Extrusion Line Produced Types of Corrugated Pipes
SingleWall Corrugated Pipes: Lightweight and flexible, used for drainage and electrical conduits.
DoubleWall Corrugated Pipes: Consist of a smooth inner wall and a corrugated outer wall for added strength and flow efficiency.
MultiWall Corrugated Pipes: Used for heavyduty applications requiring high strength and durability.
GET A QUOTATION NOW
Corrugated Pipe Extrusion Line Produced Corrugated Pipes Applications
Drainage and Sewage Systems
Electrical and Telecommunication Conduits
Agricultural Drainage
Road and Highway Drainage
Industrial Ventilation and Ducting
Advantages of Corrugated Pipe Extrusion Lines
High production efficiency and automation.
Ability to produce pipes with varying diameters and wall thicknesses.
Consistent product quality and durability.
Costeffective for largescale manufacturing.