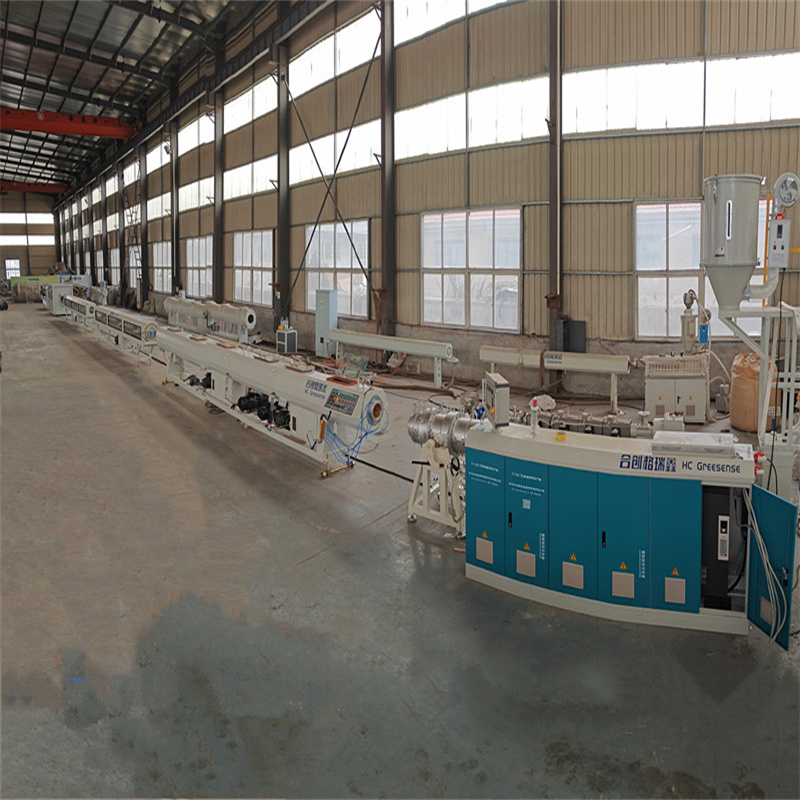
Corrugated Pipe Production Line
Send Inquiry
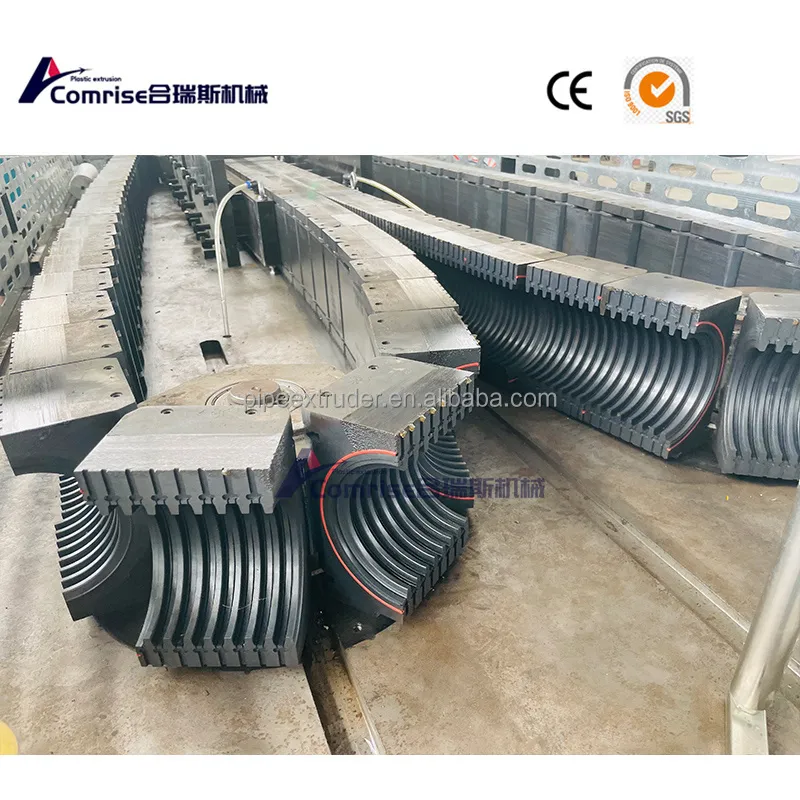
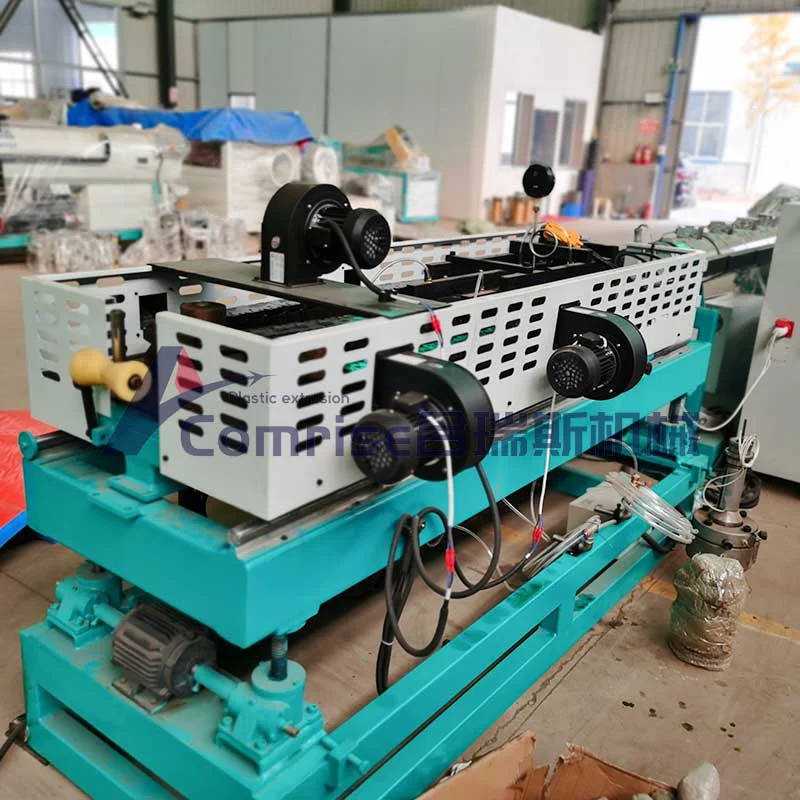
Fancy Corrugated Pipe Production Line Components:
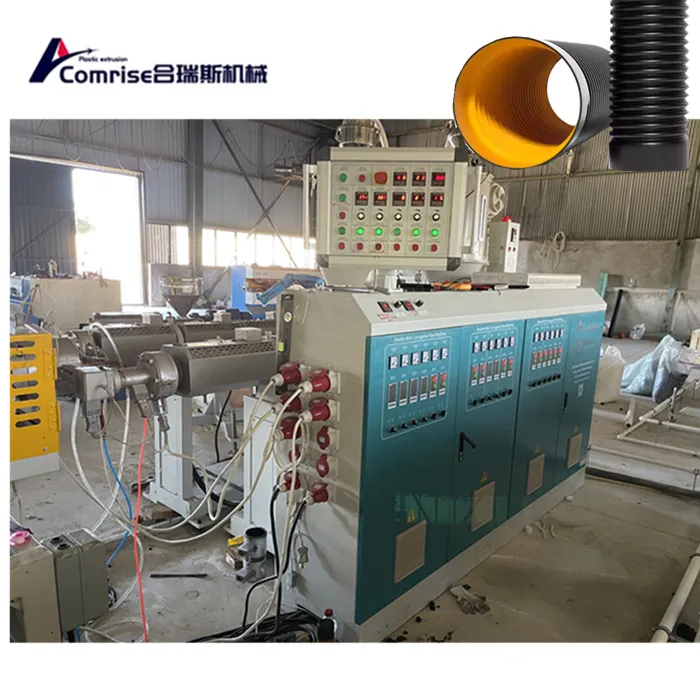
1. Extruder: The core component where raw materials (typically HDPE, PVC, or PP) are melted and formed into a continuous pipe.
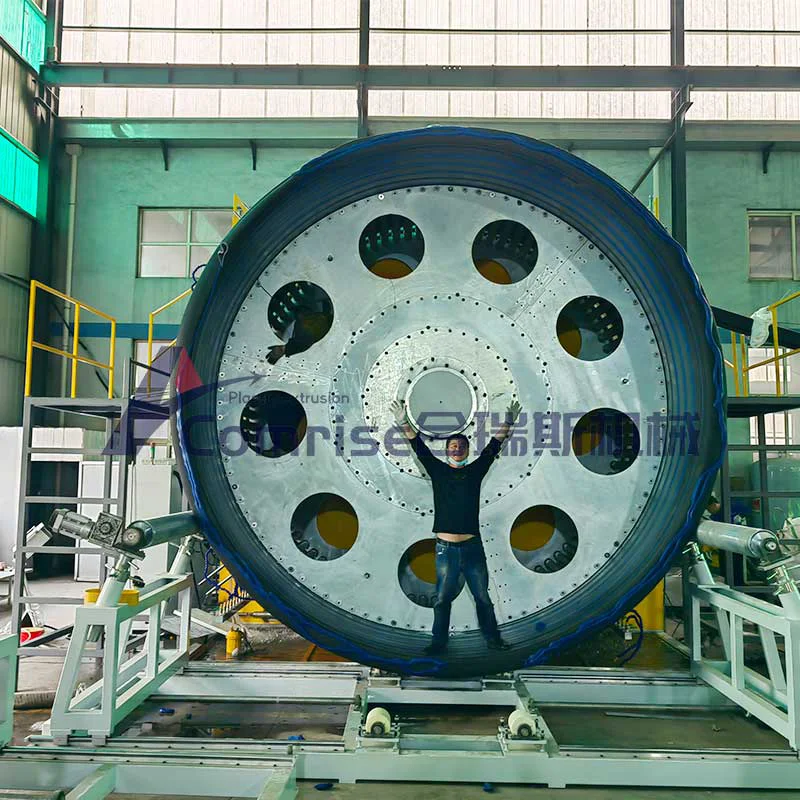
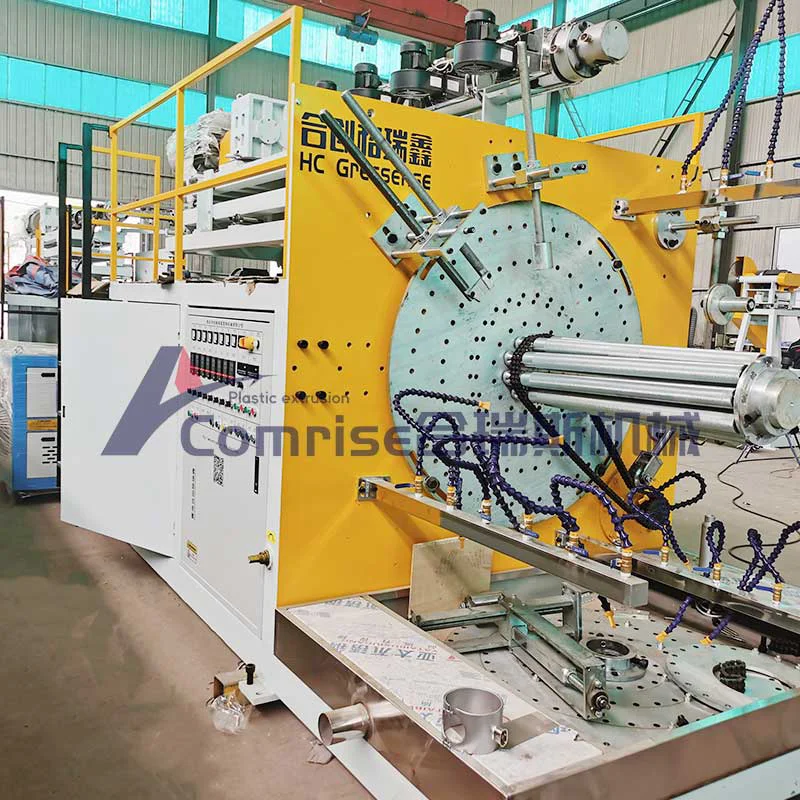
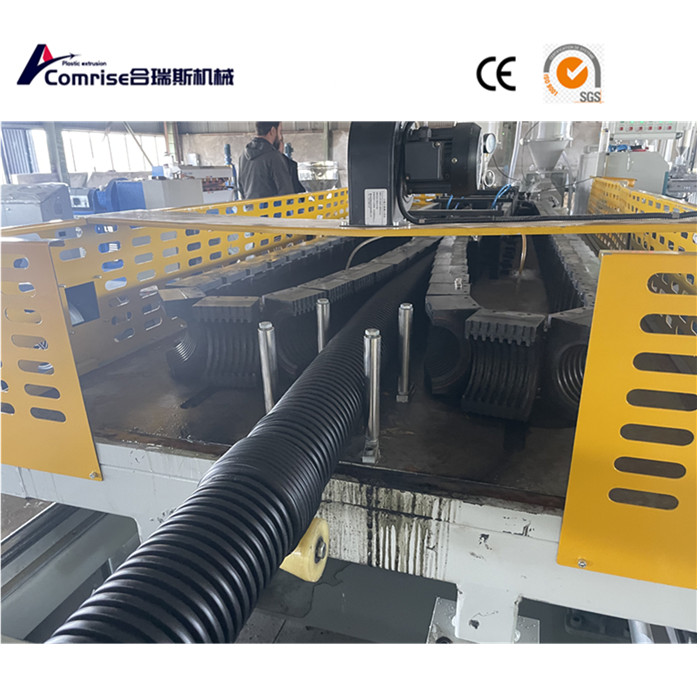
2. Corrugator: Shapes the molten pipe into a corrugated form using molds and vacuum cooling.
3. Cooling System: Cools the corrugated pipe to solidify its structure.
4. Haul-Off Unit: Pulls the pipe through the production line at a controlled speed.
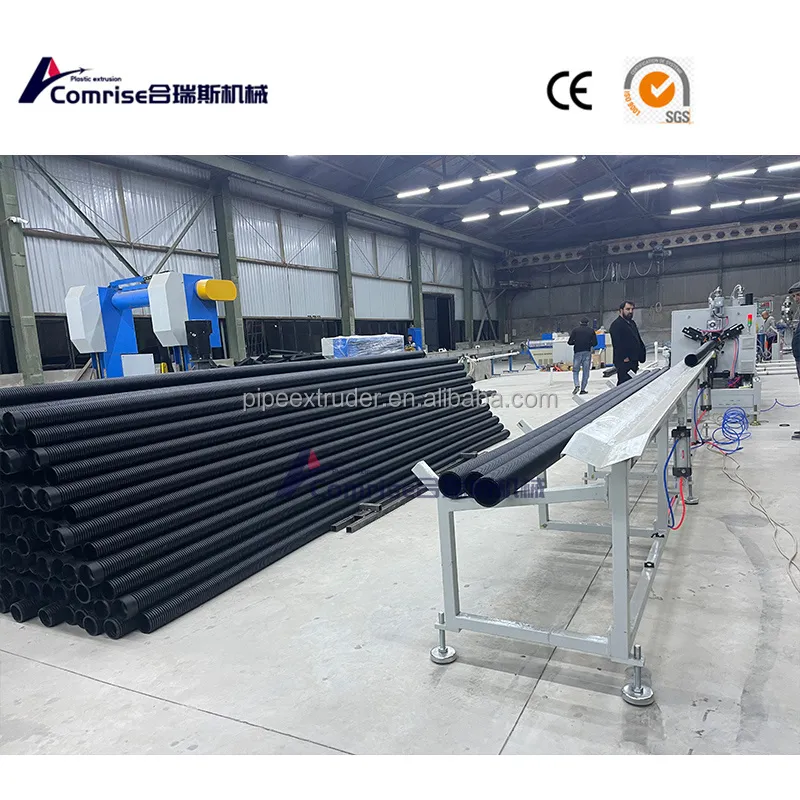
5. Cutting Unit: Cuts the pipe into desired lengths.
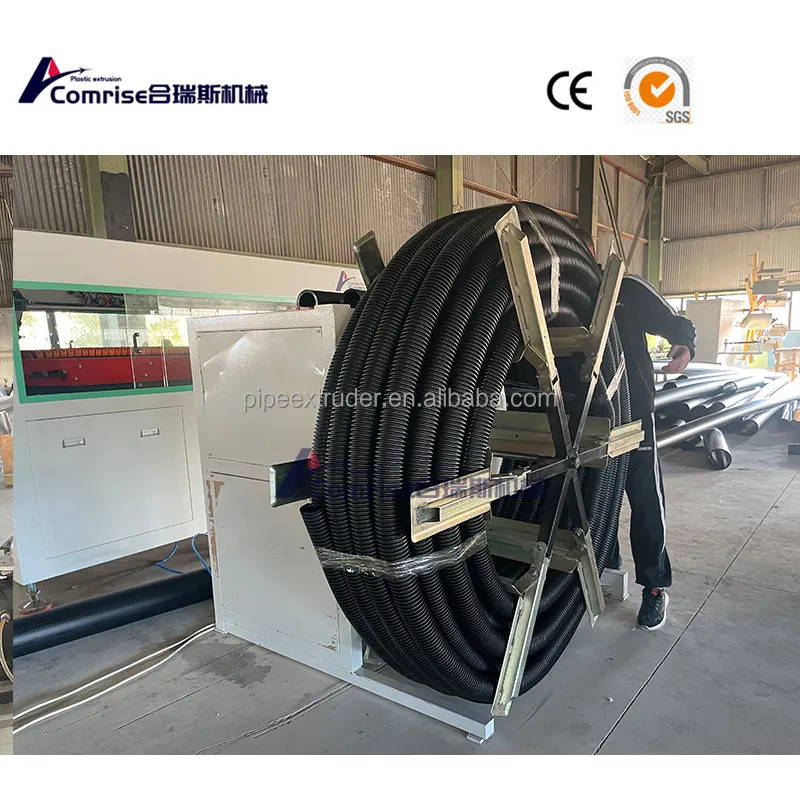
6. Stacking or Coiling Unit: Collects the finished pipes for packaging and transportation.
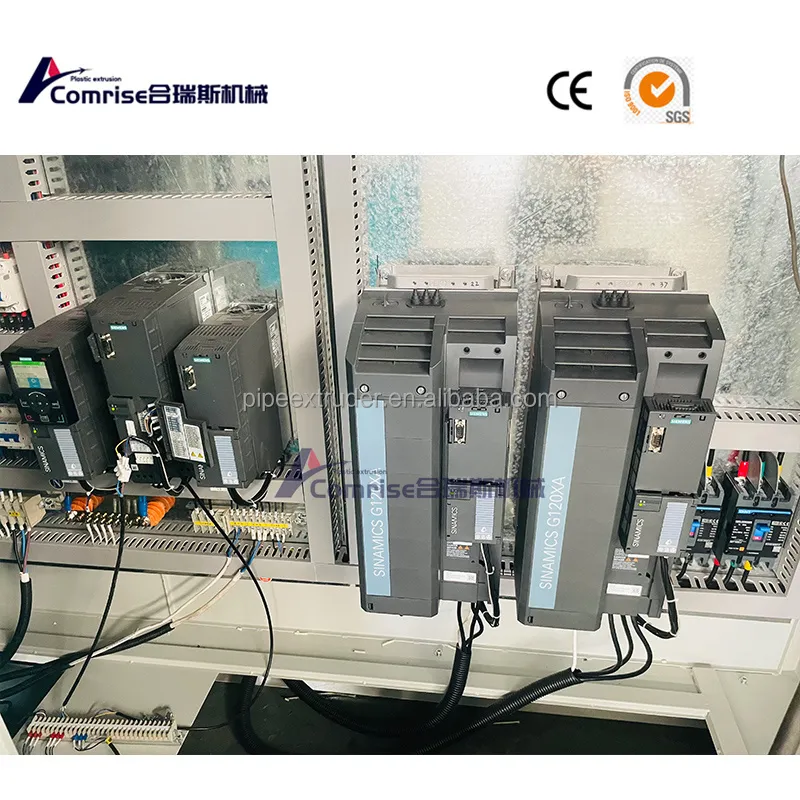
7. Control System: Monitors and controls the entire production process for precision and efficiency.
Cheap cost Corrugated Pipe Production Line Applications:
1. Drainage Systems: Used in agricultural, residential, and industrial drainage.
2. Sewage Systems: Ideal for wastewater management due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
3. Electrical Conduits: Protects electrical cables in underground and surface installations.
4. Telecommunications: Houses fiber optic and communication cables.
5. Road and Highway Construction: Provides structural support and drainage in roadbeds.
GET A QUOTATION NOW