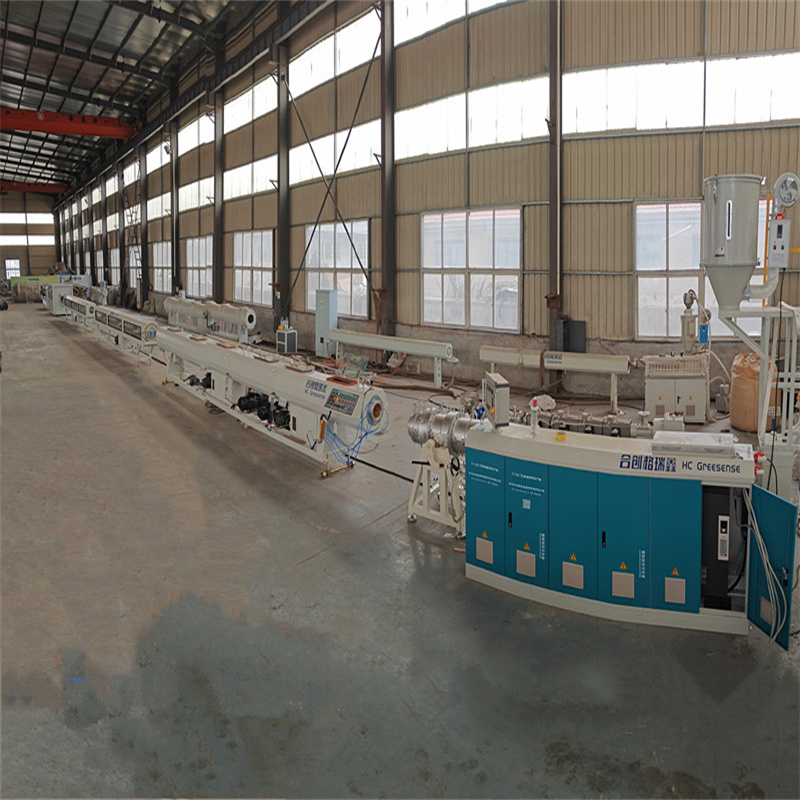
Corrugated Pipe Extruder
Send Inquiry
Corrugated Pipe Extruder Key Components and Features:
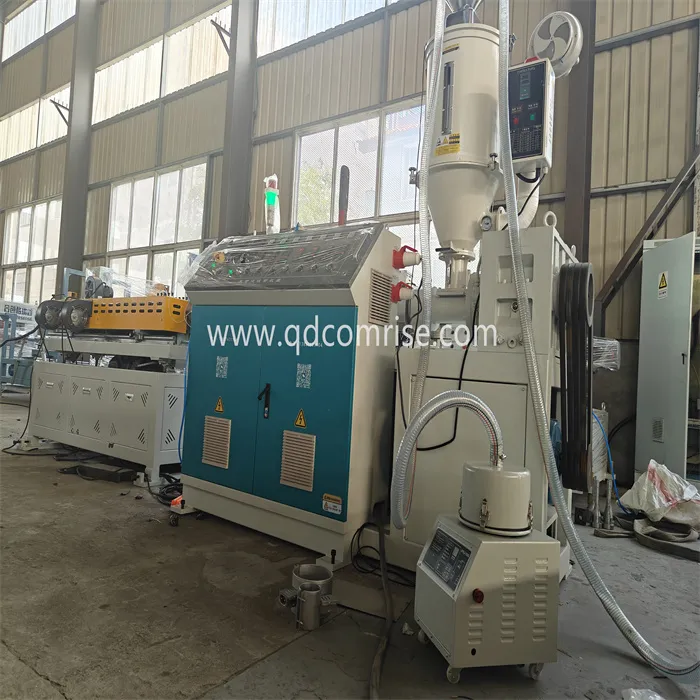
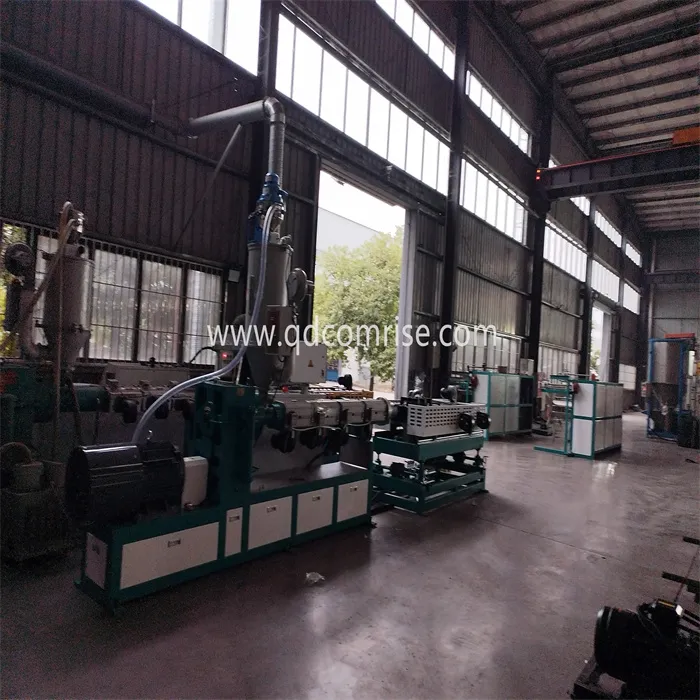
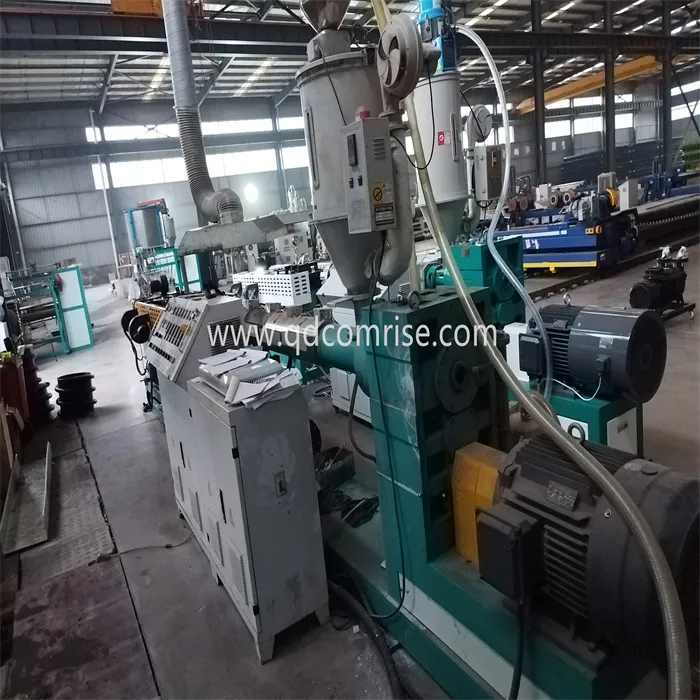
1. Extruder Unit:
Barrel and Screw: The Corrugated Pipe Extruder consists of a barrel with a rotating screw inside. The raw material (usually plastic granules or metal) is fed into the barrel, where it is heated and melted.
Heaters and Temperature Control: The barrel is equipped with heaters and temperature control systems to ensure the material is melted uniformly.
2. Die Head:
The molten material is forced through a die head, which shapes the material into a continuous pipe.
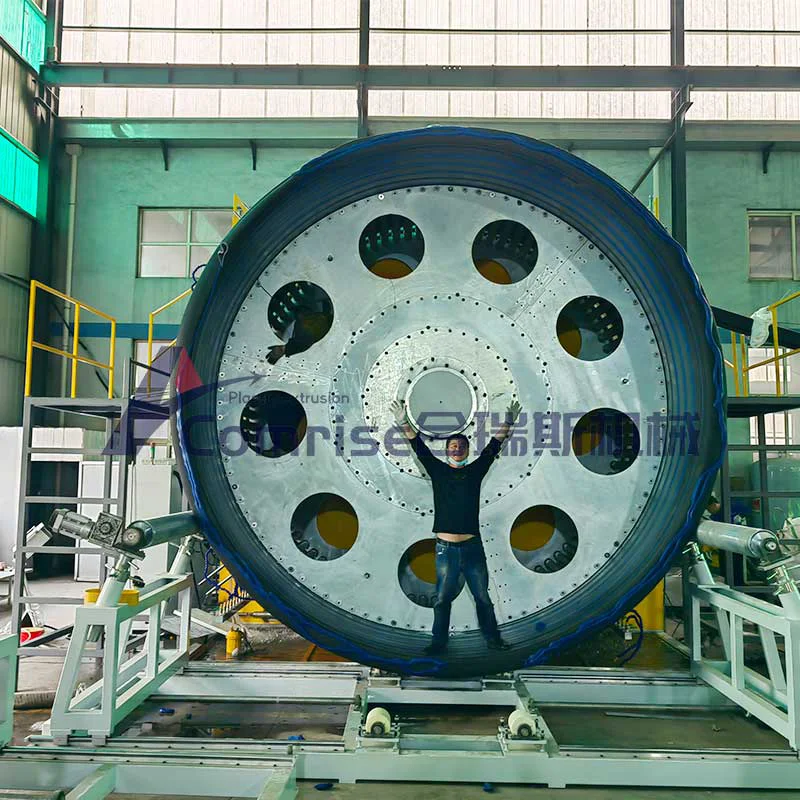
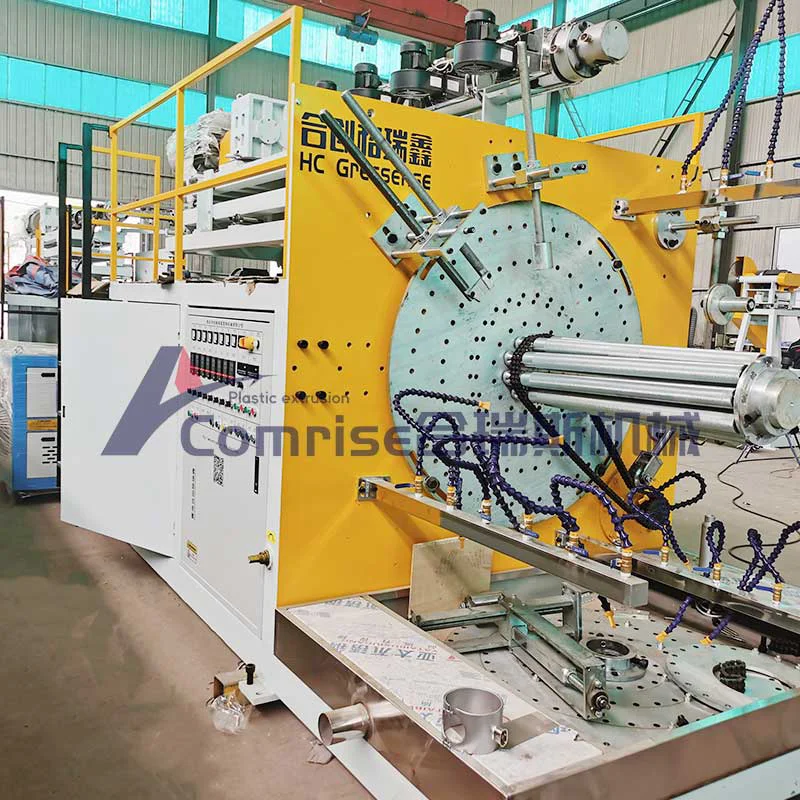
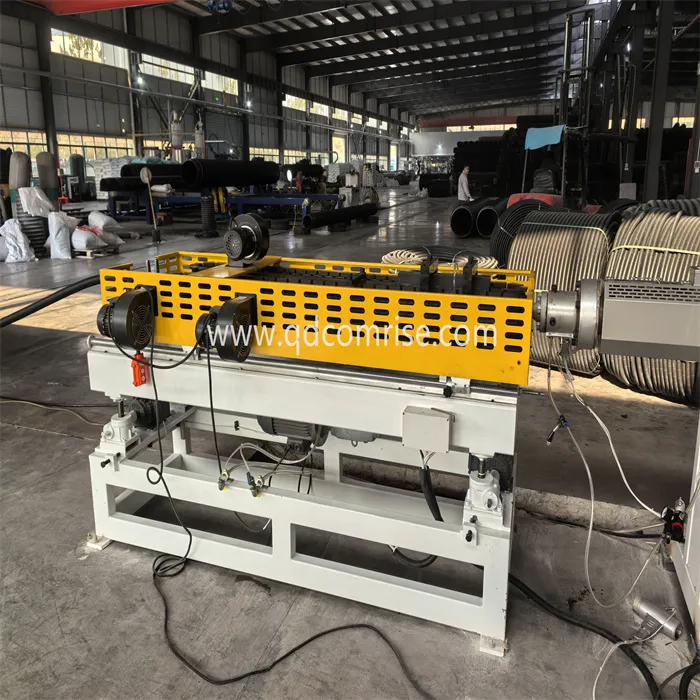
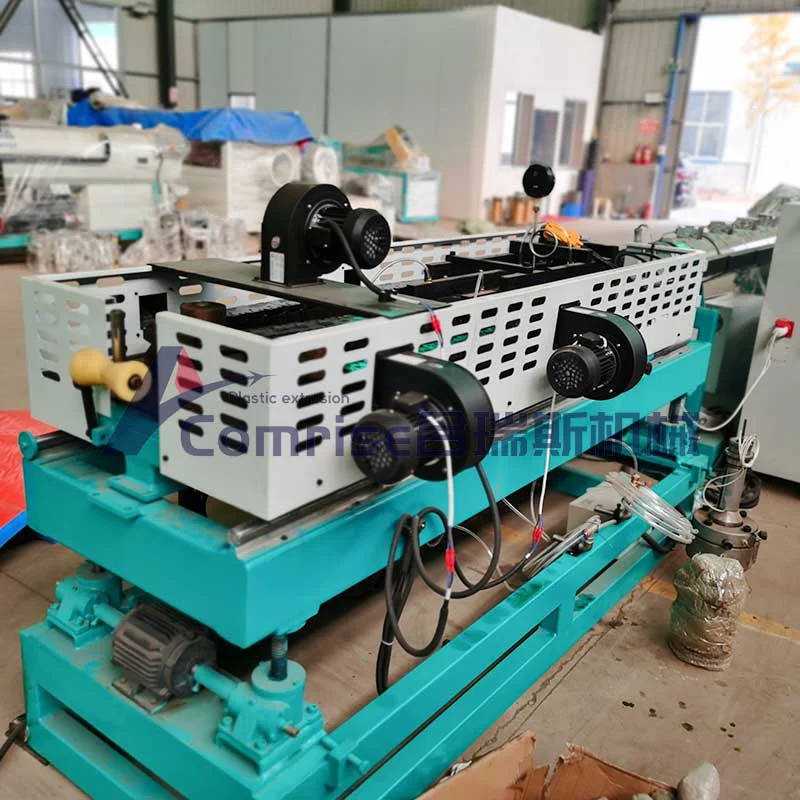
3. Corrugation Forming Unit:
Corrugated Pipe Extruder forming unit consists of a series of molds or forming mold blocks that shape the melton material into the desired corrugated pattern as it exits the die head.
Cooling System: The corrugated pipe is then cooled using air or water cooling systems to solidify the shape.
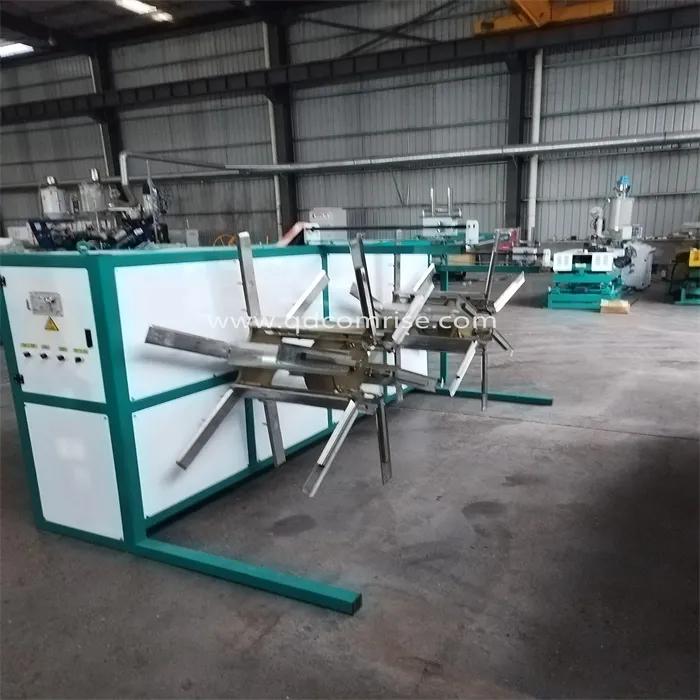
4. Pulling and Cutting Mechanism:
Puller: A pulling mechanism ensures the continuous extrusion of the corrugated pipe at a consistent speed.
Cutting Unit: The pipe is cut to the desired lengths using a cutting unit, which can be either a saw or a chipless cutter.
5. Control System:
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): Modern corrugated pipe extruders are equipped with PLCs for precise control over the extrusion process, including temperature, speed, and cutting length.
HMI (Human-Machine Interface): An HMI allows operators to monitor and adjust the machine parameters easily.